An arrhythmia is a heart rhythm that is out of sync. People with arrhythmias have a faster or slower beating heart than those without the condition. Your heart may beat abnormally for a variety of reasons, and the treatment you receive depends on the underlying cause. If your heart is racing, you’re dizzy or lightheaded, or you’re experiencing chest pain, see your doctor right away.
There may be no signs or symptoms of arrhythmia if it is “silent”. You can tell if you have an irregular heartbeat during a doctor’s examination by checking your pulse or listening to your heart.
The following symptoms were experienced by the patients with arrhythmia.
• ++Palpitations++: A fluttering or “flip-flopping” heartbeat, or a feeling that your heart has skipped a beat.
• Your heart is thumping.
• Dizziness or a feeling of lightheadedness are among the most common symptoms.
• Breathlessness.
• Pain in the chest.
• Insufficiency or exhaustion (feeling very tired).
• Low ejection fraction or heart muscle weakening.
Arrhythmias are brought on by a variety of factors.
• Coronary artery disease can cause arrhythmias.
• The heart’s irritable tissue (due to genetic or acquired causes).
• Pressure in the arteries.
• Heart muscle changes (cardiomyopathy).
• Valve malfunctions.
• Blood imbalances in electrolytes, such as sodium or potassium.
• Heart attack-related injuries.
• The process of recovery following cardiac surgery.
• Other health issues.
In order to confirm the presence of an irregular heartbeat, some of the following tests may be performed:
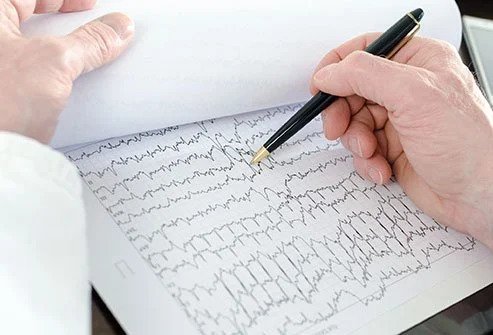
• Heart muscle electrical impulses are depicted on an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). Electrodes (small, sticky patches) are placed on the chest, arms, and legs to record an ECG on graph paper.
• Monitoring devices such as the Holter monitor.
• Arrhythmias that begin or worsen during exercise are recorded in a stress test, which is also known as an exercise stress test. An arrhythmia may be linked to underlying heart disease or coronary artery disease, which can be detected with this test.
• Any arrhythmia can be diagnosed with an echocardiogram, which is an ultrasound that shows the heart in order to check for any heart muscle or valve disease. With or without activity, this test can be administered.
• Percutaneous coronary angioplasty (PCA)
This procedure involves inserting a thin, flexible tube into the patient’s blood vessel and using an X-ray to guide it to the heart’s chambers. Through the catheter, a contrast dye is injected to produce X-ray images of your coronary arteries, heart chambers, and valves. This test can help your doctor determine if coronary artery disease is the cause of an arrhythmia. This test can also tell you how well your heart muscle and valves are functioning.
At Doral Health & Wellness Cardiology Center, we can help you find a solution for your heart problems, whether you believe they are caused by stress or are the result of underlying physical issues. As long as you’re concerned about your heart and want a second opinion, Doral Health & Wellness Cardiology Center is always ready and willing to help. Call us at 347-868-1012.